Point-to-Multipoint Communication
Point-to-multipoint (PMP) communication involves a one-to-many connection between a central device (or point) and multiple other devices (multipoint). One of the most common applications for PMP is wireless broadband. Here, fixed wireless access (FWA) providers use a relatively small number of base nodes (the points) to provide broadband Internet access to a large number of subscriber units (the multipoints).
In this guide, the wireless networking experts at MBSI WAV discuss how PMP fixed wireless broadband works, the advantages of point-to-multipoint FWA for both providers and subscribers, and the best PMP FWA solutions to help you achieve these benefits.
| Table of Contents |
What Is Point-to-Multipoint Fixed Wireless Access?
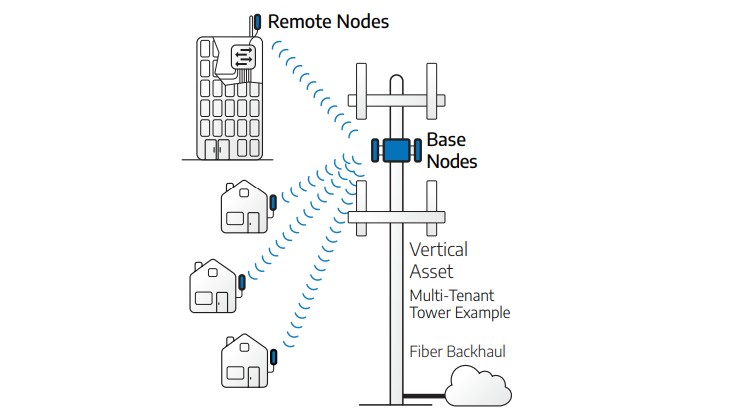
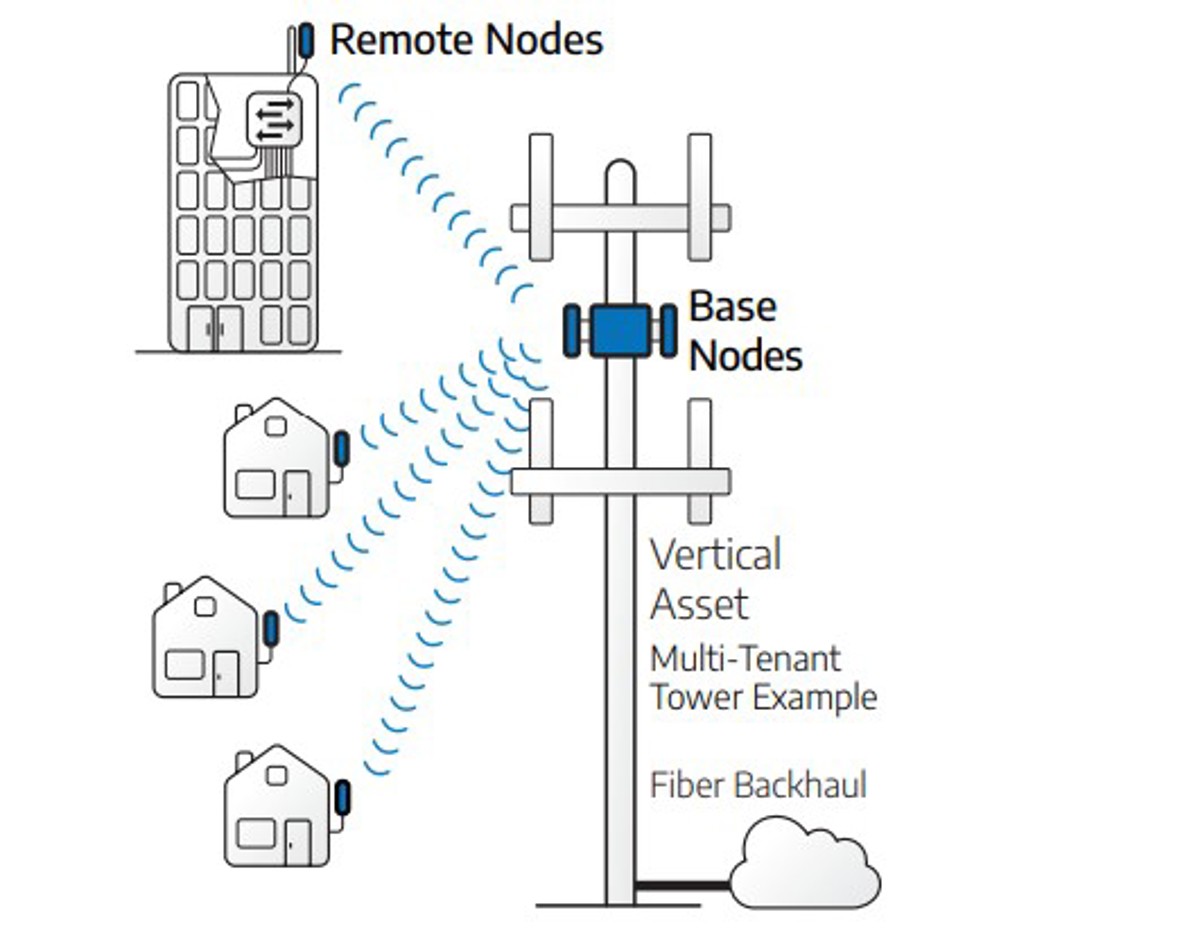
Fixed wireless access is a method of delivering broadband internet access using lightly licensed or unlicensed 3.65GHz, 5GHz and 6GHz frequencies rather than fiber or other wired technologies. FWA broadband providers strategically deploy base stations (also known as base nodes) on cellular towers, poles, or buildings; these base stations communicate with subscriber units (also known as remote nodes or customer premises equipment) installed in homes and businesses. This application of point-to-multipoint communication allows providers to reach a large number of users, even in rural or tribal communities, without the expense and hassle of running cable to every customer site.
The Benefits of Wireless Point-to-Multipoint Communication
| Benefit | Description |
| Lower Deployment Costs | Deploying point-to-multipoint FWA is less expensive because there are fewer (if any) cables to lay, and equipment can be installed on existing infrastructure. |
| Faster Implementations | Implementing point-to-multipoint FWA for last-mile Internet access is faster because subscriber units can connect as soon as a base station activates. |
| Increased Scalability | Scaling point-to-multipoint FWA is fast and cost-effective because individual base nodes can service dozens or hundreds of remote nodes. |
| Broader Coverage | Point-to-multipoint FWA provides coverage in areas where installing wired infrastructure is too difficult, helping to bridge the digital divide in underserved communities. |
Lower Deployment Costs
Deploying point to multipoint FWA is less expensive than fiber and other wired infrastructure because there are fewercables to lay. Service providers install FWA base stations on existing cellular radio towers rather than building new ones, and install subscriber units on telephone poles, streetlights, or the sides of buildings. These factors keep labor and permitting costs down, so providers begin generating revenue faster and can pass the savings along to their customers.
Faster Implementations
Implementing PMP fixed wireless access for last-mile internet access is much faster than trenching and laying cables to reach every subscriber’s home and business. As soon as a service provider activates a base node, any customer premises unit in range immediately gains Internet access. PMP FWA’s quick implementation gives service providers a faster ROI and helps local governments accelerate broadband connectivity initiatives to bridge the digital divide in rural and remote areas.
Increased Scalability
A single FWA base node provides wireless broadband Internet access for dozens or hundreds of subscriber units, allowing service providers to expand their customer base quickly and cost-effectively. When the subscriber density becomes too great, or a provider wants to expand their coverage to another geographic area, installing new base nodes is much faster and less expensive than fiber infrastructure. New subscribers get the benefit of accelerated Internet provisioning, since installing FWA customer premises equipment is also much easier than running new cable.
Broader Coverage
Point-to-multipoint fixed wireless access often works in locations where laying cable would be too difficult or cost-prohibitive because of factors like rocky terrain, restrictive land-use permitting requirements, or the extreme remoteness of the subscriber or community. PMP FWA makes it easier to expand broadband Internet access to underserved communities to help bridge the digital divide.
Advanced FWA solutions like the G1 platform from Tarana Wireless also use technology like multipath integration to ensure fast and reliable connectivity, even in non-line-of-site (NLOS) conditions when trees or buildings block the path between base units and subscriber units.
Point-to-Multipoint FWA With Tarana Wireless
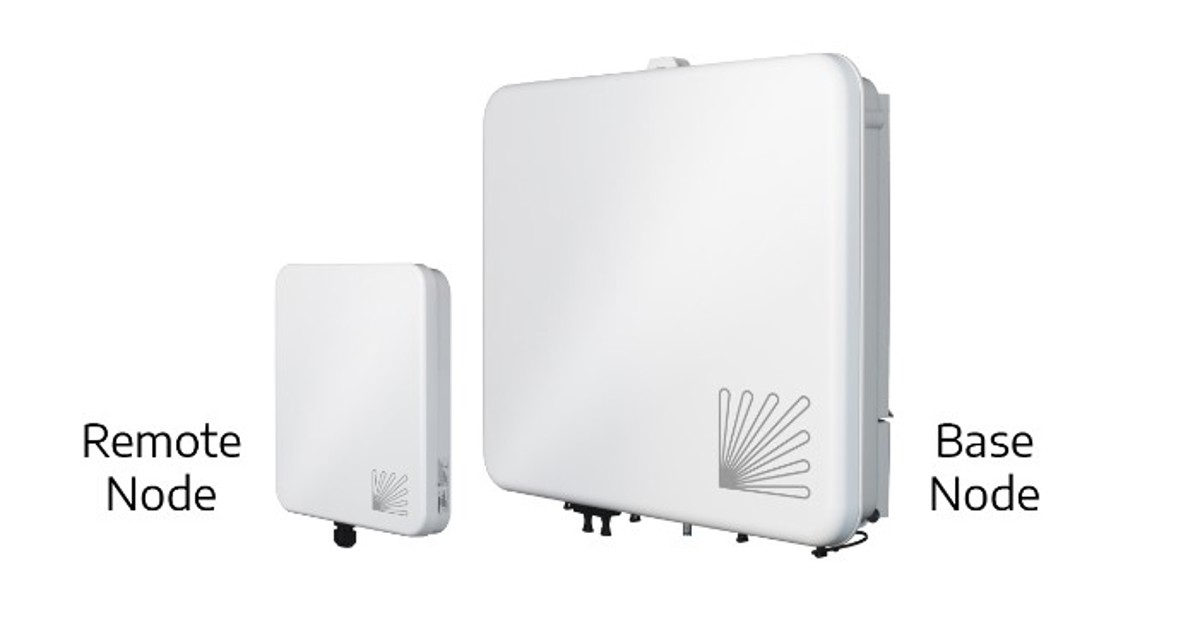
Tarana Wireless is the world’s first FWA provider to deliver next-generation fixed wireless access (ngFWA) with the G1 platform. Tarana’s wireless point-to-multipoint communication solution includes base nodes integrated with antennas, PAs, managed Ethernet switching, several teraflops of digital signal processing, and 10G optical network interfaces. Each Tarana base node services up to 256 remote nodes with up to 3.2 Gbps capacity, providing cost-effective, fiber-class Internet speeds and performance even in challenging, rural, or remote environments.

| As a trusted Tarana Wireless distributor, MBSI WAV can help you find the right FWA solutions for your use case and deployment challenges. Reach out to our world-class customer support team to learn more. |
| Contact Us |
Learn more about Next Generation Fixed Wireless Access (ngFWA)